- There are no more items in your cart
- Shipping
- Total 0.00 zł
Aeration of water is a key process aimed at improving water quality by increasing the dissolved oxygen content. This process makes it possible to support the life of aquatic organisms and effectively treat wastewater. The article will present the main objectives, mechanisms, and applications of aeration, as well as the benefits it brings to various ecosystems.
Last updated: August 26, 2025
In this article, you will learn…
Water aeration – main objectives
• Increasing the oxygen content in water – this element is essential for the life of aquatic organisms and aerobic bacteria, which participate inin biological water purification processes. • Removal of undesirable gases – aeration helps to remove harmful gases from water, such as carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, or methane. • Reduction of pollutants – by improving oxygen conditions, water aeration supports biological processes that lead to the reduction of organic pollutants and certain chemical compounds.
It is worth remembering: These mechanisms are crucialfor the efficiency of aeration, as they affect the speed and effectiveness of oxygen transfer to the water.
Basic aeration mechanisms
Aeration is based on two fundamental mechanisms – diffusion and gas exchange. The first is a process in which oxygen permeates from the air into the water across the phase boundary, while the second involves the mutual permeation of gases betweenair and H2O.
Types of water aeration
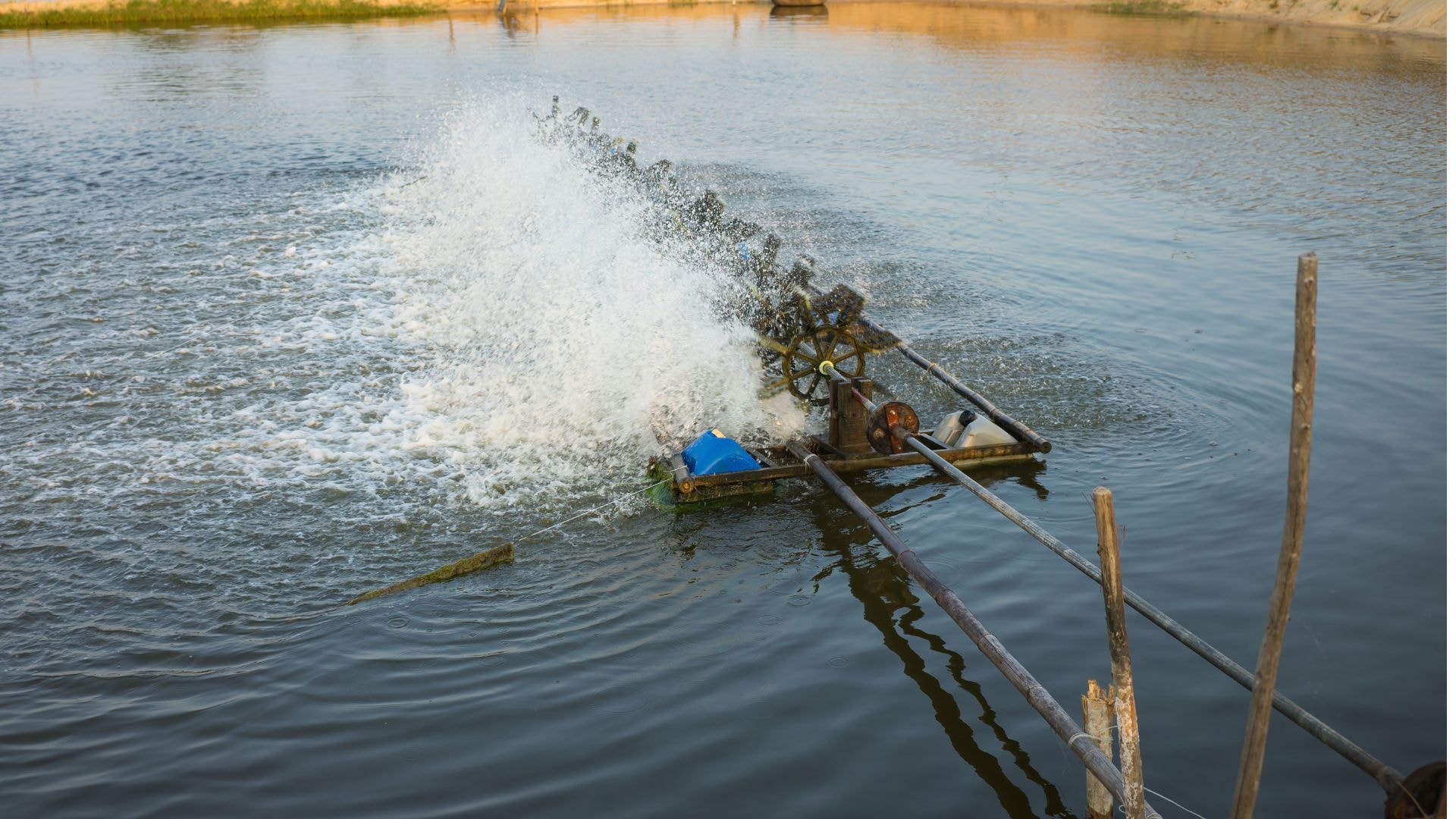
• Mechanical aeration – the procedure involves introducing air into the water using mechanical devices such as mixers, rotors, or blowers. This is one of the most commonly used aeration methods, characterized by high efficiency. • Pressurized aeration – a technique that involves introducing air into the water under pressure. For this purpose, for example,aeration columns. This is an advanced method often used in wastewater treatment systems. • Natural aeration – the result of natural processes and environmental conditions (e.g., photosynthesis of aquatic plants) to increase the oxygen content in water. This is a less intensive method, but it is important in managing the quality of surface waters.
It's worth remembering: Aerating water not only improves its quality, butalso affects the balance of aquatic ecosystems.
Benefits of aerating water
• Better water quality – one of the main benefits of aeration is the improvement of water quality. The increase in dissolved oxygen content promotes biological processes that reduce organic pollutants and improve water clarity. Aeration also helps in removing unpleasant odors and tastes caused by the presence of dissolved gases,such as hydrogen sulfide. • Support for biological processes – aeration is crucial for the functioning of biological processes in wastewater treatment plants. Oxygen is essential for aerobic bacteria that break down organic pollutants. Processes such as biological wastewater treatment, nitrification, and denitrification require an adequate level of oxygen to be effective. • Control of algae growth – in water bodies, excessive algae growth can lead to eutrophication, which meansexcessive growth of aquatic vegetation, which in turn leads to a decrease in oxygen content in the water. Aeration helps control their growth by improving oxygen conditions and supporting competitive species of aquatic plants.
Where is water aeration used?
• Wastewater treatment plants – aeration is commonly used in wastewater treatment plants as a key element of biological purification processes. In reactorsbiological processes support the activity of aerobic bacteria that break down organic pollutants. Techniques such as pressure aeration, aeration columns, or blower systems are commonly used in such installations. • Ponds and water bodies – in ponds and water bodies, aeration is used to maintain appropriate oxygen conditions, which is crucial for the health of these types of ecosystems. Artificial cascades, fountains, and blower systems areoften installed in parks and water gardens not only for aesthetic reasons but also for practical ones. • Aquaristics – aeration is essential for maintaining the health of fish and aquatic plants. In aquaristics, various aeration devices are used, such as air pumps, aeration stones, or aquarium filtration systems with aeration. • Food industry – aeration is used in the production of beer, wine, or milk fermentation. Why? This is due to the fact thatOxygen is essential for the activity of yeast and bacteria that carry out these processes.
It is worth remembering: Aeration of water is used not only in ecology but also in industry, which highlights its versatility.
Water Aeration – Summary
Aeration is one of the popular methods of water treatment, effective in removingcarbon dioxide, methane, hydrogen sulfide, or organic pollutants. This is a technology that can be successfully implemented for various applications – from small, home aquariums to advanced biological reactors used in wastewater treatment plants. In the context of growing challenges related to water quality, aeration is becoming an increasingly important element of water resource management.
Most oftenFrequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is water aeration?
It is the process of introducing air into water, which increases the concentration of dissolved oxygen.
What are the main objectives of water aeration?
Objectives include increasing oxygen content, removing unwanted gases, and reducing pollutants.
What are the types of aeration?water?
Types include mechanical, pressure, and natural aeration.
Where is water aeration used?
It is used in wastewater treatment plants, ponds, aquaculture, and the food industry.
What are the benefits of water aeration?
Benefits include improved water quality, support for biological processes, and control of growth.glonów.
What mechanisms are at work during aeration?
The mechanisms of diffusion and gas exchange are crucial for the efficiency of the process.
Author: Maciej Waliduda — a specialist in water quality and treatment technology. He has many years of experience in the industry.ecological.