- There are no more items in your cart
- Shipping
- Total 0.00 zł
The memory of water intrigues many researchers and enthusiasts seeking answers to the question of whether water can store information about the factors it has encountered. Some claim that the memory of water affects our health and daily functioning, while others view this issue with a significant dose of skepticism. In the article below, you will find explanations, water studies, controversies, and opinions on whether water may have the ability to remember.
In this article, you will learn
- What is the concept of water memory and what are its basic assumptions.
- Who was Masaru Emoto and what were his experiments with water crystals about.
- What scientific research has been conducted on water memory and what are its results.
- What arecontroversies in the scientific community regarding this phenomenon.
- How does quantum theory attempt to explain water memory?
- What is the summary and conclusions of water quality specialists on this topic?
What does it mean that water has memory?
Imagine that ordinarya glass of H₂O – in the opinion of some – **reacts to** physical, chemical, and sometimes even emotional stimuli. The concept of water memory suggests that water can store traces of substances, energy, or information it has come into contact with. Proponents claim that the structure of water undergoes changes, possibly of a temporary nature, or perhaps more permanent.
The essence of the idea that water has memory **is**the belief that even after the removal of the original substances (e.g., dissolved substances), water somehow "remembers" their presence. Then, in subsequent stages of contact with the human body or other biological systems, it can "transmit" the recorded information.
Explanation of the term "water memory"
The term **water memory** is mainly associated with bold theories presented in the works of various scientists and enthusiasts.The idea gained significance in the 1980s thanks to Jacques Benveniste. He advocated the **thesis** that H₂O molecules have the ability to retain the properties of an active substance, even if the water has been diluted to such an extent that the molecules of the original substance are undetectable.
In the following years, researchers attempted to prove or disprove the hypothesis that **the molecules** of water arrange themselves into special clusters capable of storing "memories" of previousof physical and energetic contacts. Some tests showed inconsistent results, which fueled disputes in the scientific community. Some researchers suggested that water **reacts to** energies and vibrations on a scale difficult to capture by standard methods.
Does water have memory? – basic assumptions and controversies
- People who believe in water memory think that its key **is** not only its chemical purity but also the "purityinformational”.
- They assume that water can continuously absorb and transmit the energies of its surroundings.
- In their opinion, there is a real **influence on water** through electromagnetic radiation, sounds, and even thoughts and words.
On the other hand, skeptics point out that **water memory** is not supported by the principles of particle dynamics. Water, being a liquid, forms and breaks bonds in a very short time, which in theiropinions prevent long-term "recording" of information. Nevertheless, the topic still fuels the imagination, and discrepancies in research results further ignite it.
Key thought: The concept of water memory suggests that water can store information about substances it has come into contact with, even after they have been removed. However, this is not a theory widely accepted in the community.scientific.
Masaru Emoto and his experiments
When the phrase "water has memory" is mentioned, many people recall the figure of Masaru Emoto and his experiments. He is a **Japanese scientist** who became famous for his photographs of ice crystals, which were said to change depending on emotional and environmental stimuli.
Who was Masaru Emoto (Emoto Masaru)?
Masaru Emoto became interestedwater in terms of its presumed sensitivity to words, thoughts, and energy. In the 1990s, he began publishing works in which he presented the results of experiments and photographs of beautiful, regular ice crystals. According to him, water is "alive" and absorbs energy from its surroundings. In his opinion, positive emotions and words, such as "love" or "gratitude," evoke a harmonious shape of the crystals. Over time, Emoto became a symbol of the movement seekingof the extraordinary properties of H₂O, although in the scientific community it has also faced sharp criticism for its research.
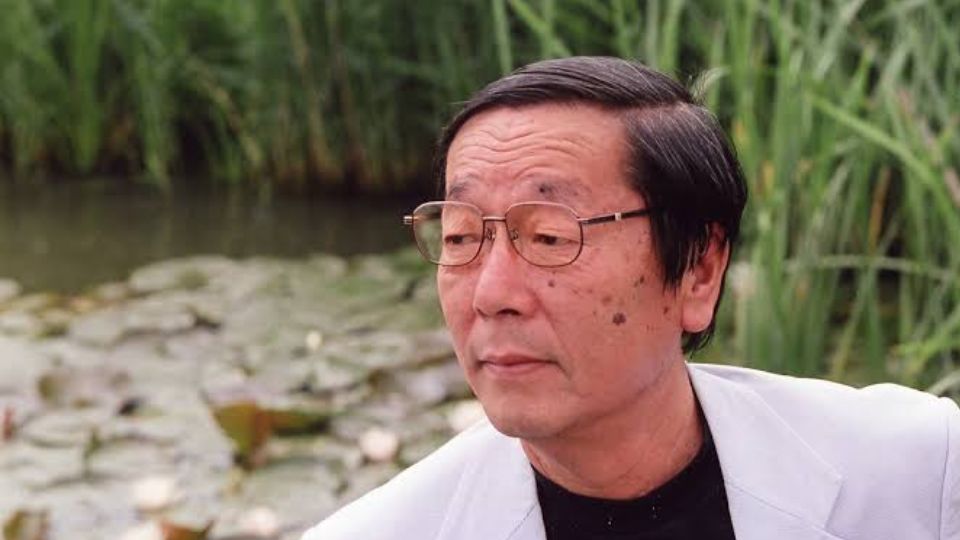

Masaru Emoto's photographic method - water images
Emoto developed a technique involving freezing water and observing its structure **under a microscope**. **Depending on** the type of stimuli (classical music, positive words, heavy rock, insults), the ice crystalstake on – according to him – various shapes:
- Water treated with words of love created beautiful, symmetrical patterns.
- Water "exposed" to negative messages froze into irregular, even ugly forms.
Some researchers claim that Emoto selected the photos subjectively. They emphasize that there are many physical factors (temperature, freezing time, pollution) that canto the shape of crystals, regardless of whether it is "exposed" to words of love or criticism.
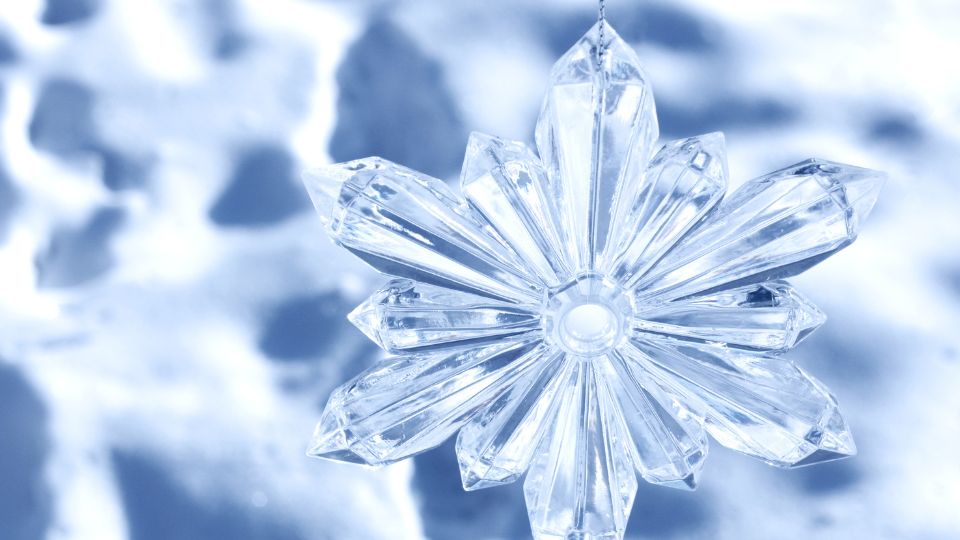

The influence of Emoto's experiments on the popularization of the theory "Water has memory"
Emoto's experiments had a huge **impact on** the awareness and imagination of people around the world. It is thanks to them that the theory of water memory **gained** such prominence in the 21st century. Although the scientists themselves often have mixed feelings aboutto the methodology of his research, Emoto contributed to the growing interest in the topic, encouraging more people to check and study the properties of H₂O.
Scientific research on water memory
Over time, many initiatives emerged aimed at confirming or refuting the water memory hypothesis. **Water studies** were conducted in various scientific centers that analyzed the **topic** of water's ability to retain molecular changes.for a longer time. The use of advanced spectroscopic devices and observational methods **under the microscope** was intended to help detect any differences in the structure of the liquid.
In **Poland** and other European countries, research projects were organized in which teams attempted to replicate dilution experiments or trace the configurations of aqueous clusters under specific temperature conditions. The results were often ambiguous, which in turn led tonutrients for turbulent discussions.
The memory of water – scientific research and its results
Here, let’s take a look at several projects and publications, **through which** scientists have tried to shed light on the issue of water memory:
- Experiments of Jacques Benveniste: It was these that sparked a global debate. Benveniste claimed that water "remembers" the presenceof biologically active substances even at extreme dilutions. Some researchers attempting to replicate his results did not confirm these observations, citing methodological shortcomings.
- Luc Montagnier's research: The Nobel Prize laureate suggested that water can record information about DNA. He believed that under certain conditions, diluted water samples emitted electromagnetic signals indicating the survival of the "signature."nucleic acid. These conclusions have met with significant interest, but also with criticism for the lack of fully reproducible results.
- Martin Chaplin's analyses: The researcher from London South Bank University has been studying the structure and behavior of water for years. In his publications, he describes the complex properties of water clusters, noting that their formation is extremely dynamic. While he recognizes the fascinating aspects of H₂O's structure, he also tempersenthusiasm, pointing out that stable molecular patterns, necessary for formulating the concept of memory, tend to break down rather quickly.
- Gerald Pollack's research on the so-called fourth phase of water: Pollack claims that there is an "Exclusion Zone" (EZ), **which** constitutes a special structure near hydrophilic surfaces. While these discoveries are intriguing and suggest more complex properties of H₂O, **even** Pollack does notit directly convinces that the memory of water in the classical sense is a fact – rather indicates the need for further research on atypical forms of liquid.
The above examples illustrate that the concept of water memory is of interest in various scientific circles, although there is still a lack of consensus regarding its validity. Some researchers see this as a signal to continue the search, while others view it as an argument for even more stringent analysis of methods.

Main experiments and conclusions regarding water memory
- The type of substance or energy that **interacts** with water is crucial in many dilution tests. Some claim that the signature of such a substance remains, **even** when chemical analysis cannot detect it.
- Many experimental groupsnoting that changes in water can be short-lived. Environmental conditions (temperature, light, pressure) can easily obscure them.
- Researchers are continuously testing the hypothesis that any potential memory of water may manifest in interactions with living organisms, such as cells or model organisms. The results are often contradictory and do not always support the claims of proponents of water memory.
These data provide a picture of **water memory** asfascinating experimental topic, in which much remains to be discovered.
Controversies in the scientific community
Many scholars put it bluntly: **to accept that water has memory, we need multiple, repeatable evidence.** One loud experiment is not enough, especially since water is a substance that constantly changes its structure. There are also doubts about the precise laboratory procedures. Critics point out that manyresearch can be burdened with statistical errors or a lack of blind trials.
Proponents counter that modern science does not yet know all the secrets of H₂O, and that the memory of water may require new research concepts and the development of more precise measuring tools. It is possible that only time and technological progress will bring definitive answers.
It is worth remembering: Although research onthe memory of water is intriguing, yet there is still a lack of repeatable, scientific evidence to confirm that water can permanently store information.
The film "The Extraordinary Memory of Water" and its significance
One of the elements popularizing the theory of the memory of water is the documentary film "The Extraordinary Memory of Water," which has raised awareness about this concept. It is a production in which various experts and enthusiasts express their views onthe topic of the hypothetical properties of H₂O. You can watch it if you want to see how this idea is presented in the media.
The film Water Memory – main assumptions and message
The film attempts to show that water holds more secrets than we usually assume. It emphasizes the potential significance of water memory in the context of homeopathy, health, and ecology. The creators present selected research findings and testimonies from people convinced of the extraordinary characteristics of H₂O.**It is worth remembering**, however, that the document has a more popular than academic character. That is why the viewer should treat it as a starting point for further, more specialized sources of knowledge.
Popularity and Criticism of the Film "The Extraordinary Memory of Water"
The film gained considerable popularity, contributing to the spread of awareness about what water memory can be. **As** in many similar cases, criticism also emerged.criticism. The accusations focus on the selective presentation of research and primarily on striking, positive results. As a result, some audiences still consider the memory of water to be a confirmed fact, while others regard it solely as an intriguing concept that is far from scientific certainty.
Memory of Water and Quantum Physics
Proponents of the theory that water has memory often refer to quantum physics. They see in quantum mechanicsa potential explanation for phenomena that cannot be easily reconciled with classical chemistry or physics. They claim that reactions between water molecules can take the form of subtle quantum effects that are difficult to observe using conventional methods.
Attempts to explain the phenomenon through quantum physics
Quantum theory posits that at the microscale, particles can be "entangled" and interact with each other in ways that go beyond classicalrights. Proponents of water memory see this as an opportunity to prove that water can serve as a kind of "carrier" of information. Critics respond that quantum mechanics in an environment as chaotic as a liquid does not provide a basis for maintaining stable systems that would store information for a longer time.
Quantum theory and its application in the context of "water has memory"
- According to some hypotheses, the electromagnetic field inWater can store energy patterns, as in the phenomenon of entanglement. Researchers are looking for correlations between quantum theory and observations of structural changes in H₂O, such as the formation of specific clusters. While quantum physics expands horizons, no irrefutable evidence has yet been found that water is a carrier of stable memory, transferred to living organisms in a predictable way.
- The idea of water memory **suggests** that molecules can store information about previous interactions, which may impact health and the environment.
- Masaru Emoto and othersenthusiasts presented fascinating hypotheses and photographs, however, some in the scientific community accuse them of lacking rigorous research procedures.
- Water studies have been conducted in many institutes – some indicate interesting properties of H₂O, while others deny that one can speak of real memory of molecules.
- The film "The Extraordinary Memory of Water" contributed to the popularization of the topic, but it is worth treating it as a starting point for further,more in-depth scientific readings.
- Attempts to explain the phenomenon of water memory through quantum physics remain theoretical – there is still no groundbreaking evidence for the permanent storage of information in water.

Our interpretation as water quality specialists
Working in the water filter industry, we look at this issue with curiosity. **It** is undoubtedly intriguing and may lead to new discoveries in the future. However, currently (in 2025), we rely on proven solutions such as professional filtration systems, UV lamps, and ionization.Are there other methods of water treatment?
We do not dismiss the possibility that future generations of scientists will discover mechanisms that we do not yet understand today. In science, it is important to keep an open mind, but also to be cautious in drawing conclusions. In our daily work, we primarily focus on reliable, tested methods of improving water quality that have concrete confirmation in laboratory studies.
Summary and conclusions
The concept of water memory remains alive despite numerous controversies. The mysteries of water have fascinated people for centuries, and researchers continue to seek out its unknown properties. The key points worth remembering are:
Although science has not yet provided unequivocal confirmations of water memory, this phenomenon undoubtedly inspires further research and reflection on the infinite complexity of H₂O. We encourage critical reading.new publications and an open mind, remembering that the beneficial properties of water are primarily related to its high quality and proper treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is water memory?
Water memory is a concept suggesting that water can store information about substances, energies, or stimuli it has come into contact with.Proponents of this theory claim that the structure of water changes, "remembering" this information even after the original factor is removed.
Have Masaru Emoto's experiments been scientifically validated?
Masaru Emoto's experiments, in which he claimed that water forms different crystals depending on the emotions conveyed to it, have not been scientifically validated. They are often criticized in the scientific community for lacking reliable methodology,subjective selection of images and the omission of many physical factors influencing the shape of ice crystals.
What do leading scientists say about water memory?
Although the concept of water memory has been studied by several scientists, such as Jacques Benveniste and Luc Montagnier, their results have faced criticism and have not been replicated in independent studies. Most of the scientific community believes that there is insufficient, repeatableevidence to consider this theory as a scientific fact.
Does quantum physics explain the phenomenon of water memory?
Quantum physics is often cited by proponents of water memory as a potential explanation for a phenomenon that goes beyond classical laws of chemistry. Critics, however, point out that the chaotic environment of a liquid, such as water, prevents the maintenance of stable quantum states that could store information for an extended period.So far, no irrefutable evidence has been found for this connection.
Does water quality have a connection with its "memory"?
In a scientific context, water memory is not considered a proven fact. Nevertheless, from the perspective of water quality specialists, its chemical and physical purity is crucial. Reliable treatment methods, such as filtration or UV lamp disinfection, are effective and proven ways to improvewater quality, regardless of the theory of its "memory".
Why did the film "The Extraordinary Memory of Water" generate such great interest?
The film "The Extraordinary Memory of Water" gained popularity by presenting a fascinating yet controversial concept in an accessible and striking way. Although it is more of a popular science material than a scientific one, it has sparked widespread social interest and prompted many people to reflect onthe mysterious properties of water.
Sources:
mojawoda.com